The Fund Regulation (FR) ontologies are an extension of the Financial Regulation Ontologies (FRO).
The diagram shows the owl:imports graph for the Investment Adviser Act files.
FRO was a 2017 legacy project that is no longer updated and supported, and the base directory, https://fundontology.com/fr/, is no longer live on the web.
However, you can download a ZIP directory of the RDF/OWL Turtle files.
The table lists the ontology files in the zip directory with their filename, prefixes, and descriptions.
The table lists the Ontology files published on this website. Just right-click on the filename to download or to copy the link into your ontology editor.
| Dir | File | Prefix | Description |
| ./ | Fund_Reasoning.ttl | fr-fund_reas | This ontology doesn’t define any triples. It is a configuration of ontology imports: |
| data/ | FR_IA_Firm_SEC.ttl | fr-ia-firm-sec | Fund Regulation Investment Adviser Firm Report instance data. |
| FundSampleData.ttl | fr-samp-data | A sample data file with fictitious Vermont financial companies. | |
| IA_Firm_SEC_Feed.ttl | ia-firm-sec | An abridged version of the SEC Investment Adviser Public Disclosure Report. | |
| form/ | IAPDSECCompilationReport.ttl | iapd-sec-cr | The Ontology Web Language (OWL) version of the Securities and Exchange Commission’s Investment Adviser Public Disclosure compilation report and form. |
| ref/ | Fund_Financial_Reference.ttl | fr-fin-ref | Investment Fund specific financial reference data. |
| Fund_Legal_Reference.ttl | fr-leg-ref | The ontology defines legal classes and properties for Investment Funds. | |
| rule/ | Rules_Investment_Adviser_Act.ttl | fr-rule-iaa | Defined classes and SPARQL rules to implement filing requirements under the Investment Adviser Act. |
Files are Ontology Web Language in Turtle notation.
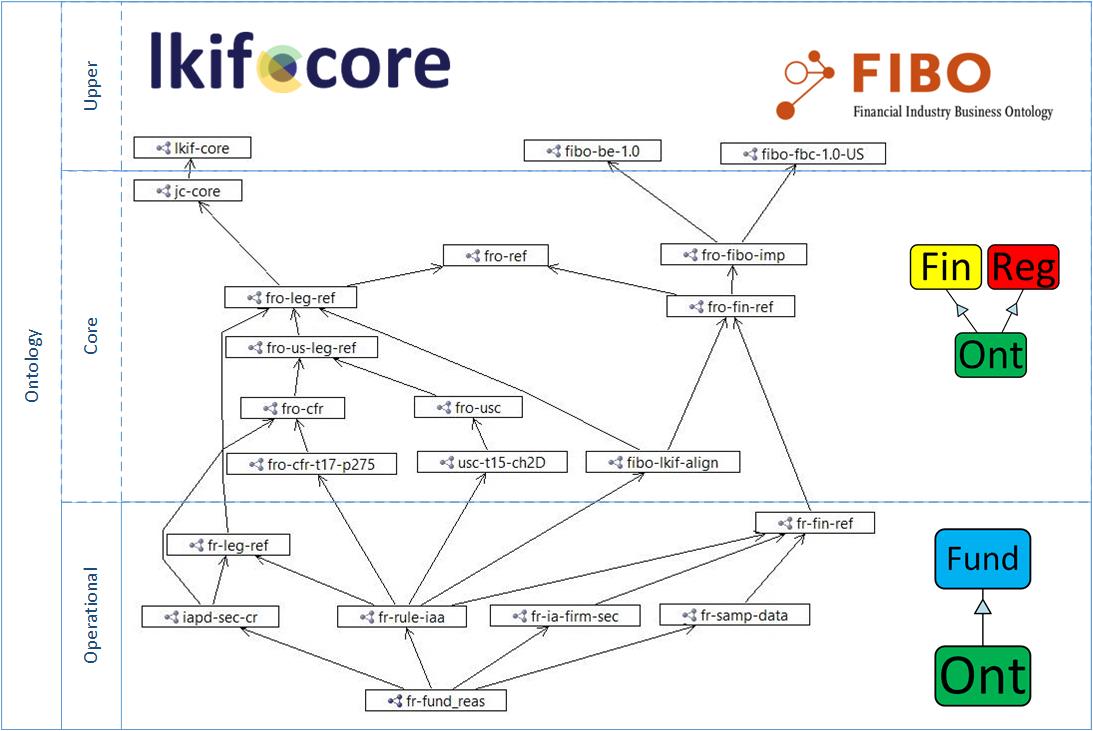
The swim lane diagram shows the include tree for Fund Reasoning.
To the left are the Ontology Layers.
- An upper ontology (also known as a top-level ontology or foundation ontology) is an ontology that describes very general concepts that are the same across all knowledge domains. Well-known core ontologies are BFO, GFO, DOLCE, SUMO, and Dublin Core. (Wikipedia)
FIBO and LKIF don’t import Upper Ontologies. They define general concepts like dates, relationships, and roles themselves. - The goal of a core ontology is to provide a global and extensible model into which data originating from distinct sources can be mapped and integrated. (Doerr, Hunter, Lagoze)
The core ontology applies to a specific domain, such as biology, medical, Legal and Finance. LIKIF and FIBO cover both the Upper and Core ontology layers. The Financial Regulation Ontology aligns and extends the Legal and Finance reference ontologies; thus, FinRegOnt is in the Core Layer. - The Operational Ontology is an implementation of a core ontology. It is specific enough to hold source data. Fund Regulation is an operational ontology for the finance sub-domain of investment management.
The boxes in the diagram depict the prefix of the ontology files (graphs).
- fr-* Fund Regulation ontology files
- iapd-* Investment Adviser Public Disclosure – the ontology files for the Compilation Report and Form ADV
- cfr-* Code of Federal Regulations – text of CFR pertaining to the Investment Adviser Act
- usc-* United States Code – text of the laws
- fro-* Financial Regulation Ontology
- lkif-* Legal Knowledge Interchange Format
- fibo-* Financial Industry Business Ontology